Author: Ronald B. Smith, MBA, PMP
Ronald Smith has over four decades of experience as Senior PM/Program Manager. He retired from IBM having written four books and over four dozen articles (for example, PMI’s PM Network magazine and MPUG) on project management, and the systems development life cycle (SDLC). He’s been a member of PMI since 1998 and evaluates articles submitted to PMI’s Knowledge Shelf Library for potential publication. From 2011 - 2017, Ronald had been an Adjunct Professor for a Master of Science in Technology and taught PM courses at the University of Houston’s College of Technology. Teaching from his own book, Project Management Tools and Techniques – A Practical Guide, Ronald offers a perspective on project management that reflects his many years of experience. Lastly in the Houston area, he has started up two Toastmasters clubs and does voluntary work at various food banks.
The INs-N-OUTs of Quality
Learn how IN-N-OUT Orvis, and quality planning, assurance, control, and improvement in IT projects can illuminate the importance of quality assurance in project management.
Reducing Risks & Boosting Quality with External Evaluations
Learn the importance of external examination by independent testing experts to find defects and ensure quality in software and hardware products.
Comparisons of a Project Manager to a Maestro
Project managers conduct their teams like maestros lead an orchestra: unifying diverse skills, setting the tempo, and delivering harmony to achieve a shared vision. Explore the parallels and improve your project management skills!
Understanding and Overcoming Limits of Project Methods
Explore the nuanced landscape of project management methods, uncovering challenges, and discovering strategic solutions to navigate limitations and ensure successful project delivery in the ever-evolving world of organizational priorities and technological advances.
The Spooky Side of Project Management
Explore the eerie parallels between Halloween and Project Management. Learn to adapt, conquer past mistakes, and tackle recurring issues. Embrace the project spirit this October and enjoy a Spook-tacular Halloween!
Consistency Gives Self-Discipline Its Power
Explore the vital role of discipline and consistency in project management, and how these core values drive success.
EPM Spelled Out
Understand the basics of Enterprise Project Management and how organizations can determine when to implement EPM for better project success.
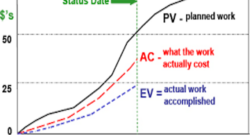
A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Earned Value Management
Learn the fundamentals of Earned Value Management (EVM) and discover how it provides a powerful tool for project managers to measure progress and make informed adjustments.